Gross National Happiness (GNH) is Bhutan’s development–philosophy. It teaches us about the important of balancing needs of the body and mind, respect for our culture and the environment and to become good, responsible citizens of Bhutan.
What are the 4 pillars and 9 domains of GNH?
The 4 pillars of pillars of GNH are all about: Good Governance, preservation of culture, sustainable socio-economic development and preservation of environment.

Sustainable socio-economic development: Its emphasis on work, economic success and sharing with other for tommarrow. A thriving GNH economy must value social and economic contributions of households and families, free time and leisure given the roles of these factors in Happiness.
Preservation of culture: It is all-knowing one’s identity, history, culture and values. Happiness is believed to be contributed to by the preserving the Bhutanese culture. Developing cultural resilience, which can be understood as the culture’s capacity to maintain and develop cultural identity, knowledge and practices, and able to overcome challenges and difficulties from other norms and ideals.
Good Governance: It is talking about the leadership, rules and regulations and responsible citizens to promote the wellbeing of all future Bhutanese.
Good Governance is a considered a pillar for happiness because it determines the conditions in which Bhutanese thrive. While policies and programs that are developed in Bhutan are in line with the values of GNH, there is also several tools and processes used to ensure the values are indeed embedded in social policy.
Preservation of environment: It mainly highlights about respecting nature, avoiding wastage and having compassion for all sentient beings. Environmental Conservation is considered a key contribution to GNH because in addition to providing critical services such as water and energy, the environment is believed to contribute to aesthetic and other stimulus that can be directly healing to people who enjoy vivid colours and light, untainted breeze and silence in nature’s sound.
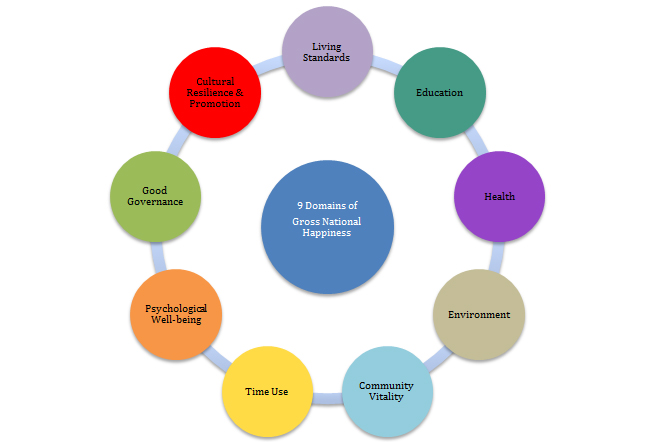
The four pillars are further elaborated into nine domains, which articulate the different elements of GNH and form the basis of GNH measurement, indices and screening tools.
- Living standards?
- Education
- Health
- Environment
- Community Vitality.
- Time-use.
- Psychological well-being.
- Good Governance
- Cultural resilience and promotion.
These 9 domains show that from the perspective of GNH, many inter-related factors are important in creating the conditions for happiness.
For example, GNH counts the importance of material security as one of these – and assessing whether people enjoy sufficient and fair living standards is included in the GNH survey. Similarly, the happiness of human beings is not seen as separate from the wellbeing of other life forms, and it includes ecological diversity and resilience in the measure of GNH. The balance between material and non-material development, and the multi-dimensional and interdependent nature of GNH are key features that distinguish GNH from GDP as a measure of a country’s progress.
Under these 9 domains, Bhutan has developed 38 sub-indexes, 72 indicators and 151 variables that are used to define and analyse the happiness of the Bhutanese people.
How can we put GNH in action?
We can put GNH in action, we have to be mindfulness, know our values, be compassion and take responsibility and show leadership. It’s simple we can put GNH in action through; respecting your parents, teachers and elders; promoting, reducing and by proper disposal of waste; being truthful and having right thoughts, view and action; taking care of your health and happiness; stop bullying in your schools/colleges; being punctual in your assignments, eat less junk food, eat more home-cooked meals; taking pride in your history and culture; and practice loving speech and listening.
References
GNHC (n.d). What is GNH? Retrieved from http://www.gnhcentrebhutan.org/what-is-gnh/the-4-pillars-of-gnh/
 1273
1273